Do AI-Generated Content and Influencer Marketing Work in the Japanese Market?

- 1. Are Influencer Campaigns Actually Driving Purchases?
- 2. Which Product Categories Sell Best Through Influencers?
- 2-1. The Top Purchase Category is Food & Beverages, Followed by Fashion, Electronics, and Cosmetics
- 2-2. TikTok and Instagram Show Strong Category Suitability
- 3. Is AI-Generated Content Influencing Purchase Decisions?
- 4. What Emotions Do Japanese Consumers Hold Toward AIGC?
Have you ever wondered, while planning your SNS strategies, “Will Japanese users truly accept AI-generated content?” or “Do influencers really drive purchasing decisions?”
For overseas brands, the Japanese market is far from straightforward—culturally and emotionally. This is especially true in rapidly evolving areas such as AI technology and influencer marketing, where relying only on qualitative impressions can easily lead to misjudgment.
In this article, we draw on the latest survey of 149 Japanese SNS users to uncover the reality and strategic insights of AI-generated content and influencer initiatives. We will explore these findings through three lenses: purchasing behavior, emotional receptivity, and platform-specific characteristics.
Are Influencer Campaigns Actually Driving Purchases?
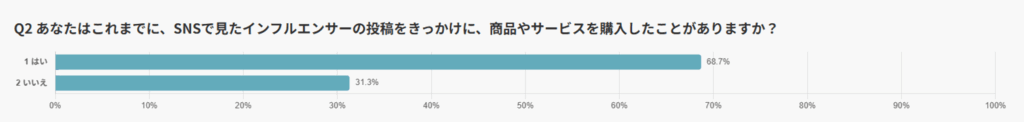
In this survey of 149 SNS users, 68.7% reported having purchased a product or service as a result of an influencer’s post.
This indicates that influencers are not merely objects of admiration or sources of reference, but that their influence directly translates into actual purchasing behavior.
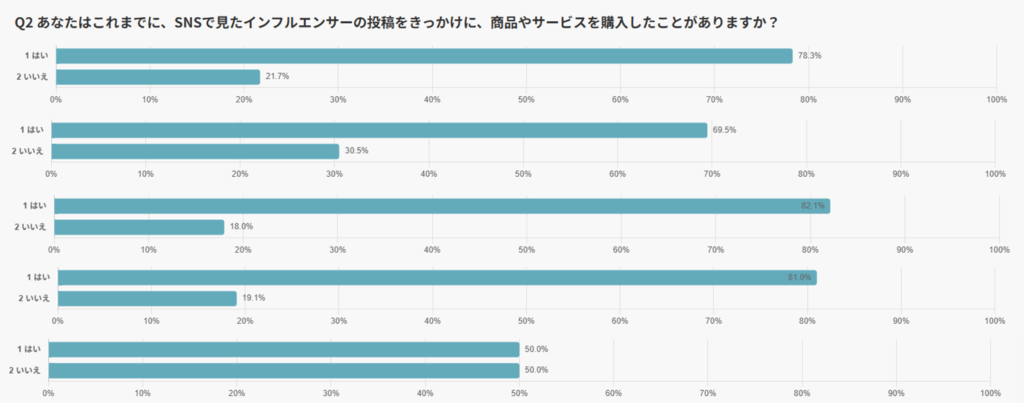
Notably, the three platforms TikTok (82.1%), X (81.0%), and Instagram (78.3%) showed purchase experience rates of around 80%, demonstrating that influencer campaigns serve as highly effective channels for driving conversions.
These findings clearly show that social influence on SNS extends beyond “awareness” or “empathy” and directly impacts consumer purchasing decisions.
It is also important to note the differing tendencies by platform. For instance, TikTok excels at dynamic appeals through short-form videos, making it well-suited for triggering impulsive purchases, while Instagram is more effective for “consideration-driven” campaigns that emphasize aesthetics and brand storytelling.
By understanding the varying purchasing-driving strengths of each channel, marketers can gain valuable insights for optimizing ROI.
Ultimately, success lies not simply in hiring influencers, but in carefully considering “who to engage, where, and how.”
Which Product Categories Sell Best Through Influencers?
Among users who had purchased a product or service as a result of SNS, certain categories stood out with notably higher figures.
In this section, we will take a closer look at the trends by product category as well as the compatibility of each with different platforms.
The Top Purchase Category is Food & Beverages, Followed by Fashion, Electronics, and Cosmetics
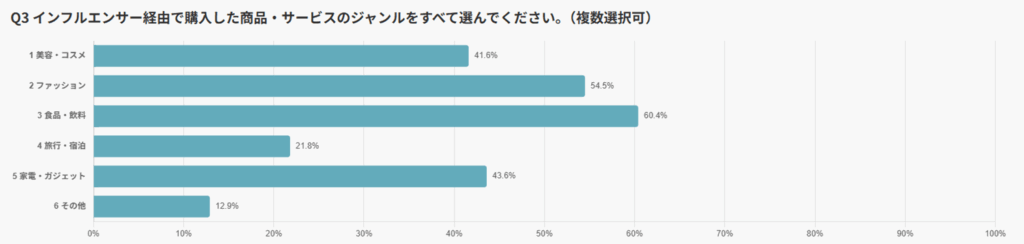
The most common purchase category overall was “Food & Beverages” (60.4%).
This was followed by “Fashion” (54.5%), “Electronics & Gadgets” (43.6%), and “Beauty & Cosmetics” (41.6%).
These categories all share a strong visual appeal, making them highly compatible with promotion on SNS.
Food tends to drive short-term purchases and, with its relatively affordable price range, is easy for consumers to try casually. Categories such as fashion, cosmetics, and electronics place great importance on usage imagery and visual presentation. When influencers introduce these items by showcasing how they are actually used, it enhances credibility and stimulates stronger purchase intent.
For brands with strengths in specific categories, understanding these differences in consumer receptivity can be a decisive factor in the success of SNS initiatives. Knowing which categories consumers rely on SNS for when making purchase decisions should be the starting point for strategy.
TikTok and Instagram Show Strong Category Suitability
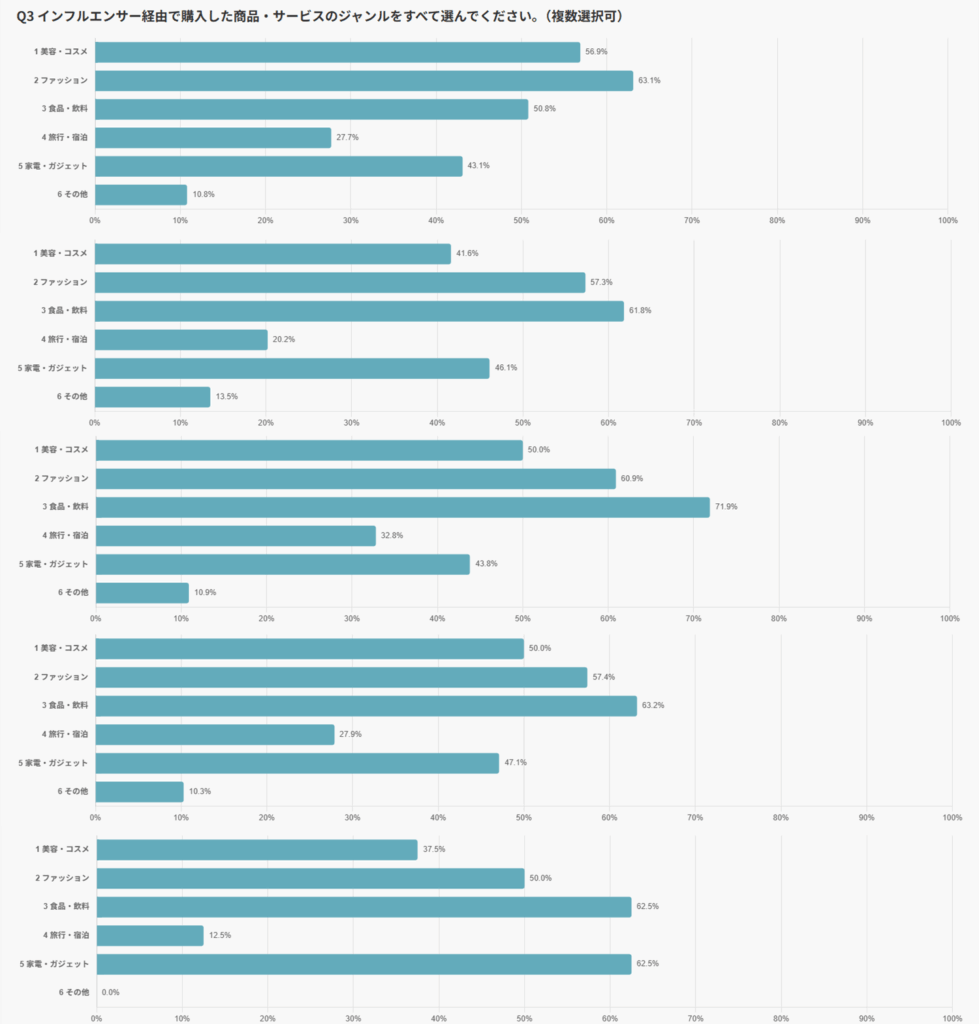
When examining purchasing trends by category across different platforms, the unique characteristics of each channel become even clearer.
On TikTok, purchase rates were particularly high for Food & Beverages (71.9%) and Fashion (60.9%). This suggests that TikTok’s distinctive ability to convey product usage scenes and features intuitively through video plays a strong role in stimulating purchase intent.
Meanwhile, on Instagram, the categories of Fashion (63.1%) and Beauty & Cosmetics (56.9%) showed high purchase rates, underscoring Instagram’s role as a platform with strengths in visual aesthetics and brand storytelling. Formats such as image-based posts and Stories are especially well-suited for products that require consumer comparison and consideration.
In this way, aligning the characteristics of the product category with the way each platform is used allows for more effective outcomes. Success lies not merely in choosing popular channels, but in strategically considering “what to communicate, to whom, and on which platform.”
Is AI-Generated Content Influencing Purchase Decisions?
How do purchasing behaviors differ between AI-generated content (AIGC) and human-created content?
In this survey, we compared impressions of decision-making speed by asking: “Which type of content makes you want to purchase a product or service more quickly?”
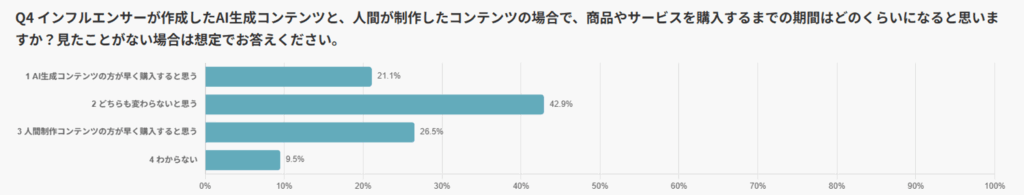
The most common response was “I think there is no difference” (42.9%).
This was followed by “I would purchase more quickly with human-created content” (26.5%) and “I would purchase more quickly with AI-generated content” (21.1%).
For many users, it is not whether the content is created by AI or humans that matters most, but rather the quality of the content itself and the timing of exposure.
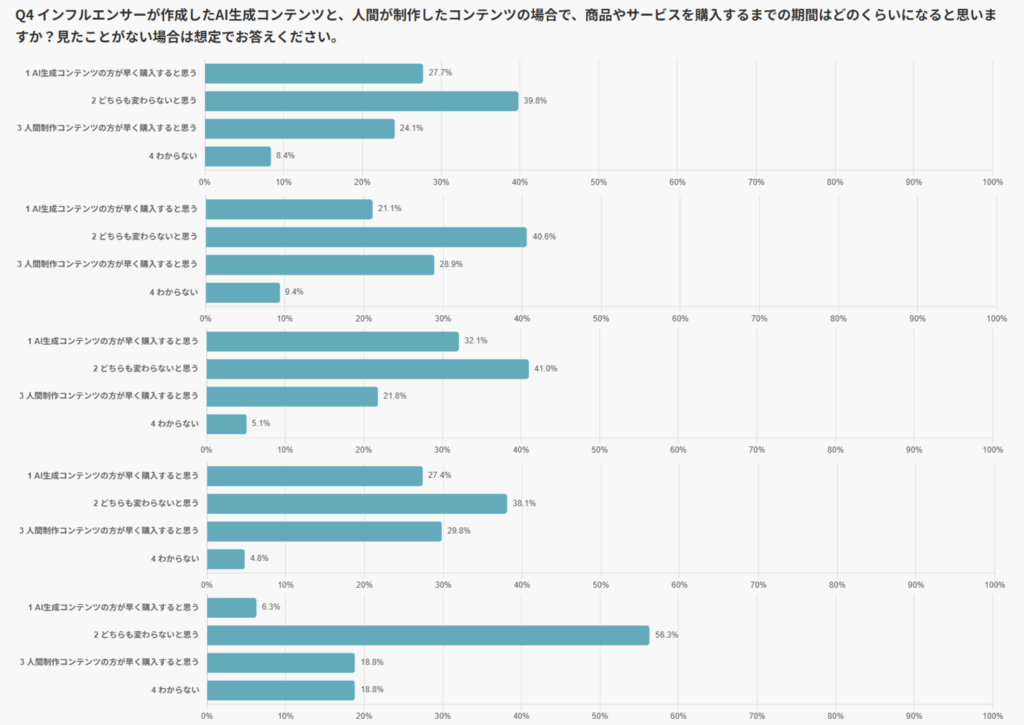
However, differences emerged when looking at results by platform.
Among TikTok users, 32.1% responded that they would purchase more quickly with AI-generated content, indicating a more positive perception of AIGC compared to other platforms. Accustomed to short-form videos, TikTok users tend to respond quickly to fast-paced visual information and show less psychological resistance to AI-driven expressions.
One noteworthy aspect is the “overwhelming scalability” of AI, which enables immersive and continuous exposure to information.
Since AI can generate a large number of visuals in a short time, users are repeatedly exposed to similar aesthetics or compositions. This makes it easier to spark a “subtle but lasting” purchase trigger, where consumers realize: “Somehow, it stuck in my mind” or “Before I knew it, I wanted it.”
This approach is difficult to achieve with human-created content due to time and cost constraints, highlighting a unique strategic advantage of AI.
Therefore, the effectiveness of AIGC cannot be measured by a simple binary of “AI vs. human.”
Instead, what truly determines success is who receives the content, at what timing, and in which format—designing context-driven experiences is key.
Rather than being constrained by the preconception that “AI is less trustworthy,” marketers should explore strategies that focus on volume, distribution, and experiential pathways enabled by AI.
What Emotions Do Japanese Consumers Hold Toward AIGC?
Clarifying users’ awareness and emotional impressions of AI-generated content (AIGC) is directly linked to risk management in campaign design.
Here, we explore the “emotional temperature” Japanese SNS users hold toward AIGC.
76.5% of SNS Users Report Having Seen AIGC
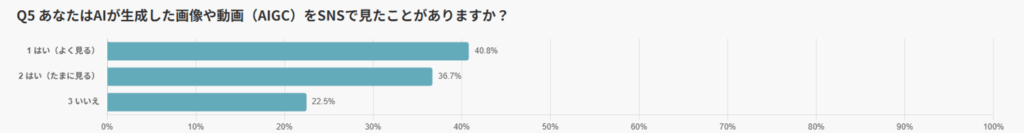
Regarding awareness of AI-generated content (AIGC), 77.5% of respondents said they had seen it — with 40.8% answering “often” and 36.7% “occasionally.” This reveals that a large majority of users are already encountering AIGC in some form.
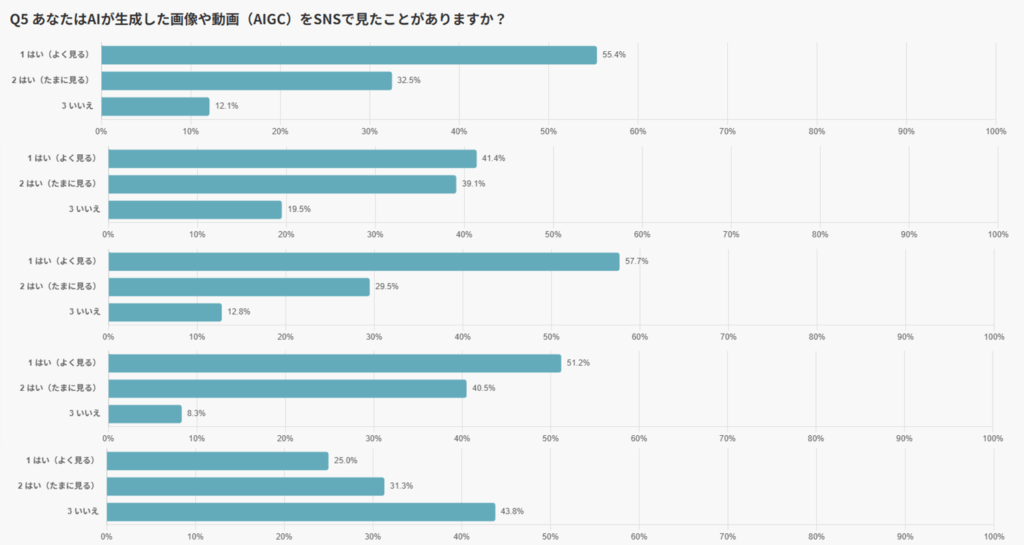
By platform, the figures were even higher: X (91.7%), Instagram (87.9%), and TikTok (87.2%), showing that more than 80% of users on major visual-centric SNS platforms reported having seen AIGC. This indicates that its presence is widely established across these channels.
These results suggest that AIGC is already becoming integrated into users’ feeds as a “natural part of the information stream.” Even without emphasizing that “this was created by AI,” the content has reached a level of quality where users experience little to no sense of discomfort, meaning the barrier of awareness is already being overcome.
The Majority Feel ‘Indifferent’ Toward Influencers Using AIGC
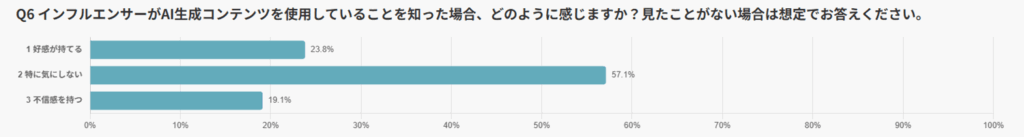
When asked about their impressions of influencers using AIGC, the majority of respondents answered “No particular concern” (57.1%).
A significant portion also expressed a positive view, with 23.8% saying they “felt favorable”, while only 19.1% reported “feeling distrust.”
These results indicate that many users are already accepting AI without strong feelings of discomfort.
For brands, this implies that rather than being bound by preconceptions such as “AI feels cold” or “AI seems unnatural,” a safer adoption strategy is to start by leveraging AI in areas where emotional resistance is minimal and expand gradually.
Clearly Labeling Content as AIGC Tends to Strengthen Positive Impressions
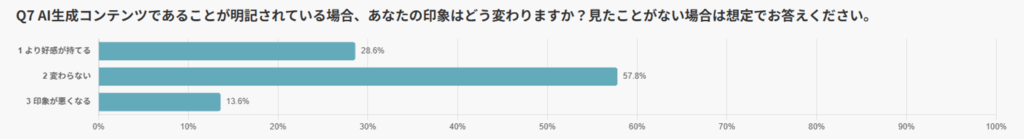
Regarding changes in impressions when content was explicitly labeled as AIGC, the most common response was “No change” (57.8%), followed by “More favorable impression” (28.6%).
Only 13.6% reported a “worse impression,” indicating that transparent labeling rarely has a negative effect.
For brands leveraging AI, it may be more effective to enhance trust through proactive transparency, rather than avoiding disclosure in fear of raising doubts.
Suitable Categories for AIGC and Its Impact on Purchase Intent
Identifying the product categories where AI-generated content (AIGC) is most effective—and understanding how it influences consumer purchase intent—is essential for building a successful utilization strategy.
In this section, we shed light on category-specific receptivity and the actual consumer behaviors stimulated by AIGC.
Strong Acceptance in Visual-Centric Categories Like Fashion
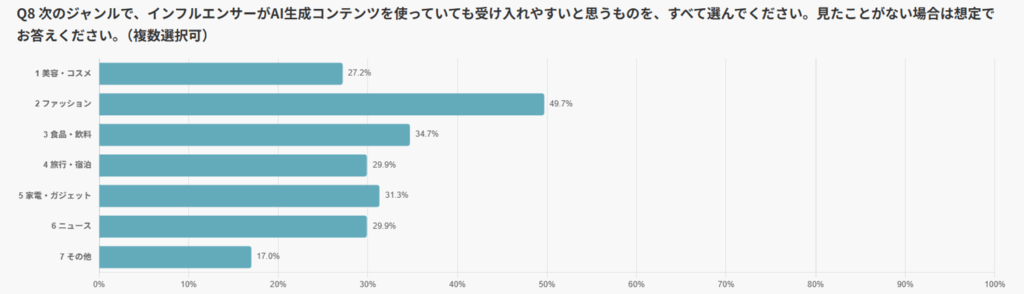
The category most frequently cited as being “easier to accept even when AIGC is used” was Fashion (49.7%).
This was followed by Food & Beverages (34.7%), Electronics & Gadgets (31.3%), and Travel & Accommodation as well as News (both at 29.9%).
What these categories share in common is that first impressions shaped by visual information strongly influence purchase decisions. In areas where visual cues are crucial—such as styling suggestions, food presentation, or product usage imagery—AIGC’s strengths in expressiveness and responsiveness are particularly effective.
When considering the adoption of AIGC, the key to maximizing results while minimizing risks lies in identifying the intersection between “the type of expression consumers expect” and “the type of expression AI excels at.”
67.3% of Users Report Increased Purchase Intent Triggered by AIGC
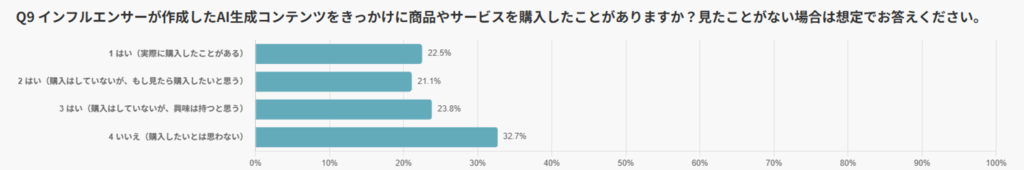
A total of 67.3% of users responded that they had either purchased or felt interest as a result of influencer posts using AIGC.
Breaking this down: 22.5% said they had actually purchased, 21.1% had not purchased but wanted to, and 23.8% said they would feel interested. These results highlight that AIGC is effectively resonating with users on an emotional level.
These findings demonstrate that AIGC is not merely a “low-cost production alternative,” but a practical marketing asset capable of sparking genuine consumer desire. Especially for reaching consumers in the early consideration stage or lighter engagement segments, AIGC can serve as a highly effective entry point.
Do Consumers Want to See More AIGC in the Future?
When assessing the future potential of AIGC, one of the key questions is: how many users actually want to see more of it?
In this survey, we asked about expectations toward AI-generated content, in order to measure both user receptivity and the market’s growth potential.
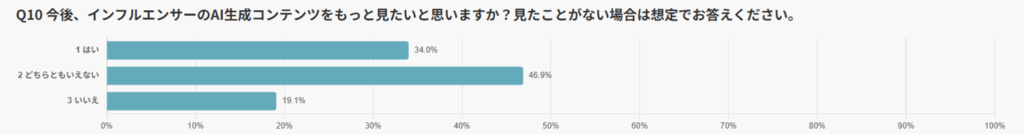
Overall, 34.0% of respondents said they want to see more influencer posts using AIGC, meaning that one in three users is open to greater exposure.
Meanwhile, the largest group was neutral (“can’t say either way”) at 46.9%, representing nearly half of respondents. Only 19.1% clearly rejected AIGC (“don’t want to see it”), showing that strong negativity remains a minority stance.
The high proportion of neutral users also suggests that attitudes may shift depending on the quality and delivery of AIGC. In other words, this field still holds significant room for growth.
A practical approach would be to start with trials or A/B testing targeted at the positive and neutral segments, gauge their responses, and then gradually expand the scope of use.
Ultimately, the timing and context in which AIGC is introduced will be the decisive factors in securing competitive advantage, as it holds the potential to become a mainstream format in the future.
Conclusion
This survey revealed a clear fact: both influencer campaigns and AI-generated content (AIGC) are already having a tangible impact on the purchasing behavior of Japanese SNS users.
They are no longer just sources of buzz but have proven to function as practical initiatives that, with the right strategy, can deliver measurable results.
First, SNS platforms serve as a foundation for daily information exposure, and beyond their high usage rates, certain platforms show a particularly strong correlation with purchasing behavior.
Going forward, it will be essential to incorporate the perspective of “how likely a channel is to drive purchases” into channel selection.
Especially in specific categories or target segments, the compatibility between the medium and the product will significantly influence campaign performance.
.png)






